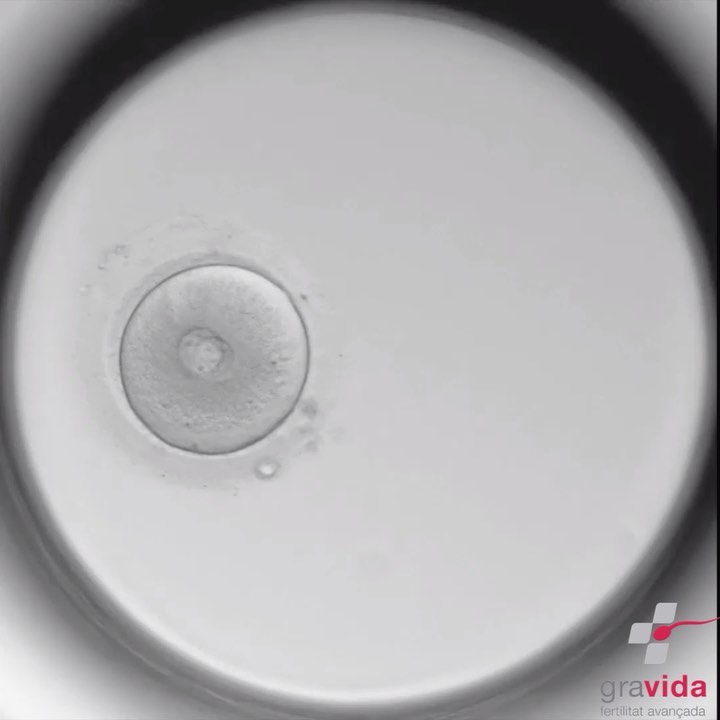
Today we would like to talk about the Time Lapse culture system, so that you can get to know all the advantages it offers, both for the embryos and for the embryologists who use it.
The Time Lapse culture system is a type of closed incubator that allows the culture of embryos avoiding, as much as possible, variations in the culture conditions, such as light, temperature or the percentage of gases to which the embryos are exposed. For an embryo to develop in the best possible way, it needs very specific conditions. These incubator try to reproduce, as closely as possible, the conditions that occur physiologically, i.e., in the mother’s womb.
What culture conditions does an embryo need?
Light
When fertilisation occurs naturally, the light conditions are very specific. For this reason, Assisted Reproduction laboratories maintain a low, very dim light, since there is no light inside the fallopian tubes neither in the uterus. Light can lead to genetic mutations, so it is a very important condition to consider in embryo culture. In traditional incubators, embryos are cultured in dark plates. However, when their evaluation is necessary, they must leave the incubator to be evaluated under the microscope (counting the number of cells, the size of the cells, the percentage of fragmentation and its distribution, the number of visible nuclei in each of the cells, the appearance and colour of the cytoplasm of the cells, etc.). For this reason, they spend a short period of time outside the incubator. On the other hand, in the Time Lapse system, embryo assessment can be performed without removing the culture dish from the incubator, thanks to the integrated recording system, which allows recording throughout embryo development.
Temperature
Embryos should be cultured at the same temperature as they would be under natural conditions. For that reason, it has been determined that the ideal temperature for their culture is 37ºC. In the Time Lapse culture system, the temperature is constantly recorded, and it is not necessary to remove the plates from the incubator to carry out the morphological assessment, so that the embryos do not suffer temperature variations at practically any time.
CO2
It has been observed that the CO2 concentration of the uterus is approximately 5%. In order to maintain these conditions during embryo culture, the incubator must be connected to gas intakes. Again, when an embryo is cultured in a Time Lapse incubator, it will not be affected by changes in the CO2 percentage.
Oxygen
To achieve the correct oxygen concentration, the incubators are connected to a gas supply that provides nitrogen gas. This element displaces the oxygen so that we reduce the ambient oxygen concentration (which is 20%) to a concentration of 5% inside the incubator.
pH
The pH is a very important factor to consider during embryo culture. For good embryo development, the pH of the culture medium needs to be between 7.2 and 7.4. Some of the culture media have components that change colour when there has been a change in pH. In this way, the embryologist can visually detect very quickly whether a change in the pH of the culture medium is occurring in that cell- culture dish.
Advantages of the Time Lapse culture system
- Variations in culture conditions, such as temperature, light, pH of the culture medium, CO2 percentage, oxygen percentage, etc., are reduced, since it is not necessary to remove the cell- culture dish from the incubator to perform the embryo assessment.
- It allows a morphokinetic assessment of embryo quality and not only a morphological one. With this system, the embryo is not only observed at a specific moment, but the recording allows the entire development of the embryo to be seen. These data make it possible to know at what exact moment the most remarkable events in the development of an embryo take place, such as the appearance of pronuclei, the first cell division, the beginning of compaction, the beginning of the blastocoelic cavity, etc. In this way, when faced with two embryos that present similar morphological characteristics, the one that has had a better development will be selected for transfer, thus obtaining greater possibilities of achieving pregnancy.
- The fertilisation of the embryos can be assessed at any time: To know if an oocyte has been fertilized correctly, it is necessary to observe a zygote with two pronuclei (one female and one male). These pronuclei appear 18 hours after fertilisation. The Time Lapse system has an advantage over traditional culture, as fertilisation can be carried out in the laboratory at almost any time. We know that the entire development will be recorded, and we can visualize it as if it were a film. For this reason, if the appearance of pronuclei occurs at any time during the night, the embryologist will not need to be present at that moment but will be able to visualize it first thing in the morning.
- Reduced evaporation of the culture medium: Although in all types of incubators the culture plates are prepared with oil in order to reduce the evaporation of the culture medium, with the Time Lapse culture system there is less evaporation. This is important, as evaporation of the medium in which the embryos are cultured can lead to variations in pH, which can negatively affect embryo development.
- The manipulation of the embryo is reduced, which implies fewer risks.
- Last but not least, those patients who achieve pregnancy can enjoy the recording of embryonic development from fertilisation to the moment of transfer, allowing future parents to know the history of their baby from the first moment of its formation. Can you imagine being able to see you when you were an embryo only hours old?
At Gravida we have different incubators with Time Lapse technology, such as Embryoscope® or Geri® and our embryologists are specialized in their daily use. If you have any doubts about this, you can arrange a visit with one of our embryologists so that they can solve them for you, as they usually do in all treatments involving embryo culture.